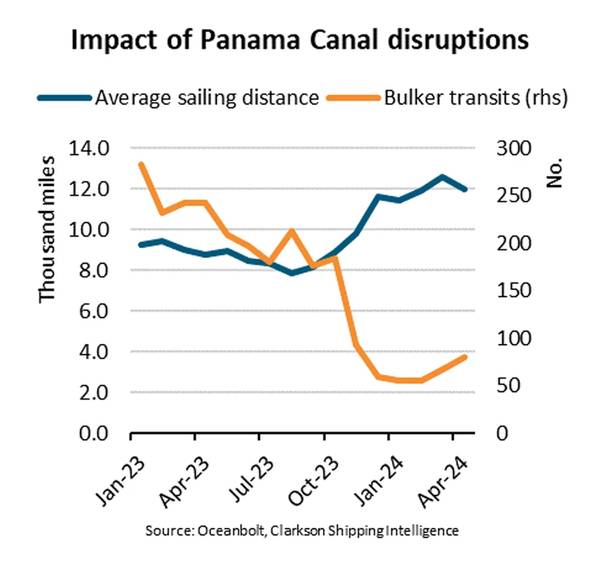
Capacity reduction on the Panama Canal have hurt dry bulk market, with dry bulk carrier transits down significantly (down 74% in the Q1 '24 vs. '23, with sailing distances up 31% and cargo volume down 25% year on year, according to BIMCO shipping analyst Filipe Gouveia.
Low water levels in lake Gatun have caused restrictions in the number of transits through the Panama Canal at a maximum draft level of 13.4m (44 ft). Under typical conditions, between 34 and 38 ships transit the canal per day at draught levels of 15.2m (50 feet). At the start of the year, only 22 daily transits were allowed. In April, however, up to 27 transits were allowed, rising to 31 transits currently.
The dry bulk sector has been particularly affected by the reduction in transits due to the market’s unpredictable nature. Unlike bulk carriers, container ships typically operate on fixed schedules, making it easier for them to book transit slots through the canal. As a result, many dry bulk operators have chosen to reroute and instead sail around the Cape of Good Hope or Cape Horn, lengthening sailing distances and boosting demand.
East Asia Trade Changes
Weaker grain shipments from the US to East Asia were the main reason why cargo volumes fell in the period. China has purchased more grain from Brazil which is usually transported around the Cape of Good Hope. Grains currently account for 34% of cargo going through the Panama Canal, most of which come from the US.
Coal, steel, fertilizers and petcoke are other important dry bulk cargoes that typically sail through the Panama Canal. Despite the restrictions, steel and fertilizer shipments through the canal have largely remained stable.
“The disruptions in the Panama Canal could soon come to an end, ahead of the maize and soya bean harvests in the US in September. On 1 June, the daily transits through the Panama Canal will increase yet again to 32 transits per day and the ongoing rainy season in Panama could lead to further increases. As conditions normalise and sailing distances shorten, we may see a decline in demand for ships on the affected routes,” said Gouveia.



